How Social Factors Shape Our Mental Well-Being
FACT CHECKED ✅
Mental health is influenced by a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors. Social determinants—conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age—play a critical role in shaping mental health and well-being. This review examines how key social determinants such as socioeconomic status, education, environment, and social support affect mental health and contribute to mental health disorders.
 |
| Social determinants play a critical role in shaping mental health and well-being. (📷: lumenlearning) |
Socioeconomic Status
Income and Employment
Socioeconomic status (SES) is a significant determinant of mental health. Individuals with lower SES often face financial stress, limited access to healthcare, and poor living conditions, increasing the risk of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Research indicates that stable employment and adequate income are protective factors against mental health issues.
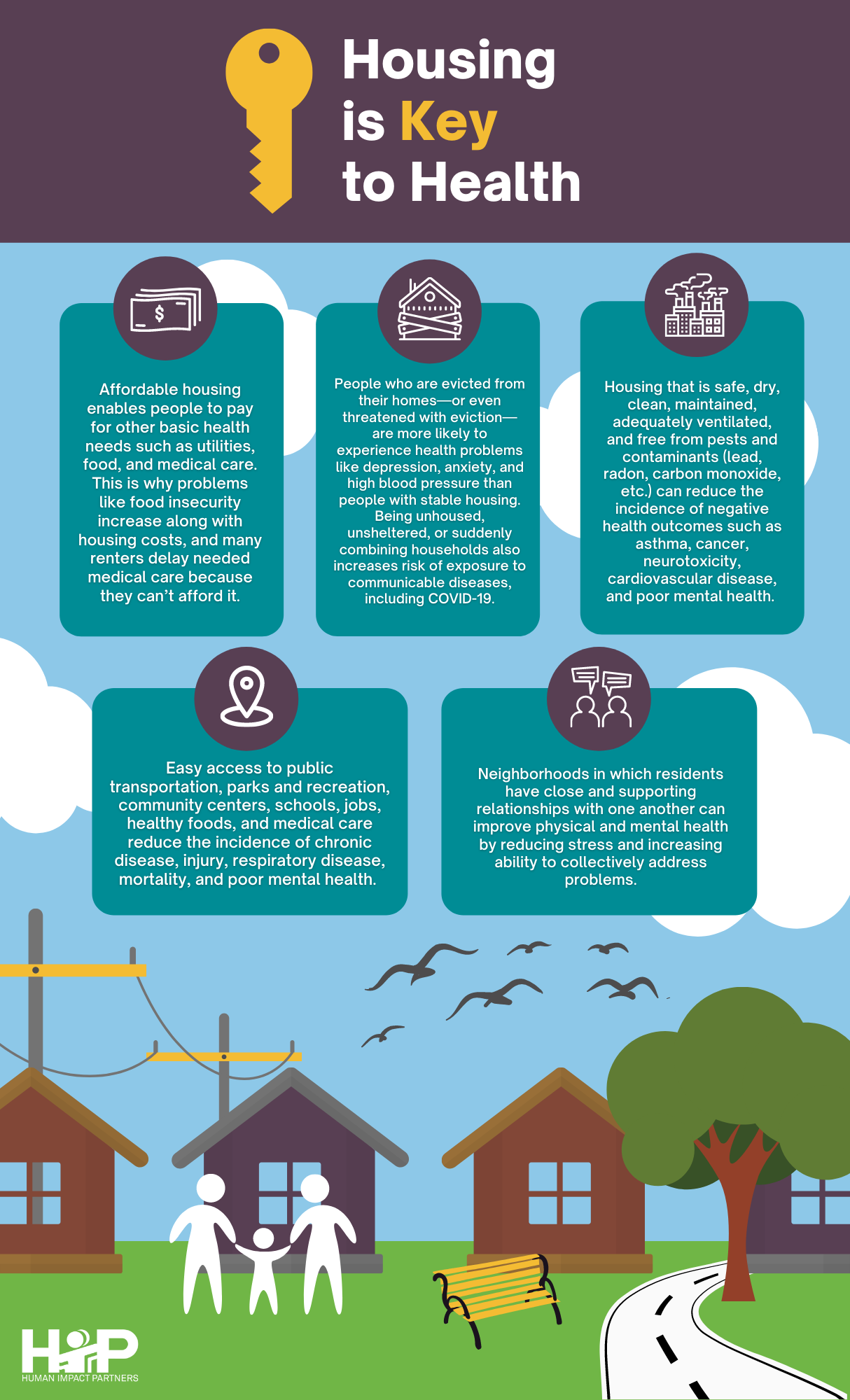
Housing Stability
Housing instability and homelessness are closely linked to poor mental health. Secure and affordable housing can provide a foundation for mental well-being, while housing instability exacerbates stress and increases the risk of mental disorders. Policies aimed at improving housing conditions can significantly impact mental health outcomes.
 |
| (📷: publichealthawakened) |
Education
Access to Quality Education
Education influences mental health by providing individuals with knowledge, skills, and opportunities. Higher levels of education are associated with better mental health outcomes. Quality education fosters cognitive development, critical thinking, and social skills, which are essential for mental resilience.
Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education plays a crucial role in shaping mental health. Programs that support early development can mitigate the effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), which are risk factors for mental health disorders. Investing in early education can have long-term benefits for mental health.
Environment
Physical Environment
The physical environment, including air quality, noise levels, and green spaces, impacts mental health. Poor environmental conditions contribute to stress and anxiety, while access to nature and clean environments promotes mental well-being. Urban planning that prioritises healthy environments can improve mental health outcomes.
Neighbourhood Safety
Perceptions of safety and actual crime rates in neighbourhoods influence mental health. Living in a safe and supportive community reduces stress and fosters a sense of belonging. Community initiatives to enhance neighbourhood safety can positively impact mental health.
Social Support
Family and Peer Support
Social support from family, friends, and peers is a critical determinant of mental health. Strong social networks provide emotional support, reduce feelings of isolation, and enhance coping mechanisms. Social support is particularly important during times of stress or crisis.
Community Engagement
Active participation in community activities and social groups can improve mental health by providing a sense of purpose and belonging. Community engagement initiatives can foster social connections and support mental well-being.
Intersectional Perspectives
Marginalised Communities
Research highlights that marginalised communities, including racial and ethnic minorities, LGBTQ+ individuals, and people with disabilities, face unique social determinants that impact mental health. Discrimination, social exclusion, and systemic inequalities contribute to higher rates of mental health disorders in these populations. Addressing these disparities requires targeted interventions and inclusive policies.
Gender and Mental Health
Gender also plays a role in shaping mental health experiences. Women are more likely to experience certain mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, often due to gender-specific social determinants like gender-based violence and unequal access to resources. Men's mental health can be impacted by societal expectations and stigma around expressing emotions. Gender-sensitive approaches are also essential for effective mental health interventions.
Policy Implications and Interventions
Integrated Approaches
Addressing the social determinants of mental health requires integrated approaches that involve collaboration across sectors such as healthcare, education, housing, and employment. Policies that promote social equity and access to resources can improve mental health outcomes.
Community-Based Programs
Community-based programs that address social determinants at the local level can be highly effective. Initiatives that provide education, employment support, safe housing, and social connections can foster mental well-being and reduce the prevalence of mental health disorders.
 |
| Mental health is influenced by a complex interplay of factors. (📷: pharmanewsonline) |
Understanding and addressing the social determinants of mental health is crucial for promoting mental well-being and reducing mental health disorders. By focusing on socioeconomic status, education, environment, and social support, we can develop effective interventions and policies that improve mental health outcomes for all individuals. Continued research and inclusive policies are essential for advancing mental health equity and fostering a healthier society.
⭐⭐⭐


